With the progress of the times, people are paying more and more attention to environmental protection, and industrial green development has become a new leading trend. Therefore, biodegradable materials are imperative. So what are bio based materials?
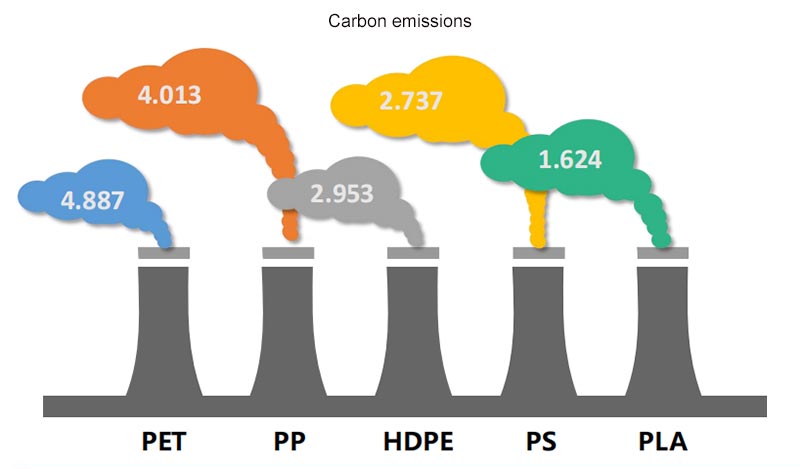
Biobased materials refer to renewable biomass resources formed through photosynthesis as raw materials, which are transformed into biological products through biological fermentation technology, and then purified and polymerized into polymer environmentally friendly biomaterials. Biodegradable materials can decompose into CO2 and H20 under microbial action or composting conditions. Compared to petroleum based materials, bio based materials can reduce carbon emissions by up to 67%.
Typical carbon emissions during the entire production process of some polymers (kg CO2/kg products):
In daily life, we cannot do without plastic products, but we all know that plastic is not environmentally friendly and is the main product of “white waste”. However, plastic products are ubiquitous in our daily lives. As a result, degradable plastics have gradually become a new trend.
To this end, scientists have developed a biodegradable product – polylactic acid. This plastic, which is converted from plant starch, has excellent biodegradability and is environmentally friendly due to its preparation process that eliminates environmentally friendly petrochemical raw materials. Polylactic acid (PLA) is currently one of the most widely used, promising, and cost-effective biodegradable materials.
What is PLA?
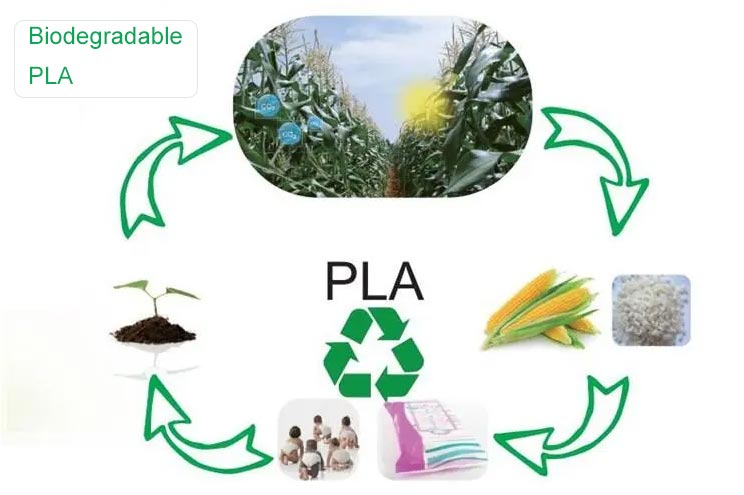
Poly (lactic acid), abbreviated as PLA, also known as polylactic acid, CAS 26100-51-6 or CAS 26023-30-3. Polylactic acid is made from biomass as raw material, originating from nature and belonging to nature. The conversion process of PLA is as follows – chemists can efficiently convert starch extracted from crops such as corn into LA through hydrolysis and microbial fermentation steps, and further convert it into PLA through condensation polymerization or ring opening polymerization, achieving the “magic” of turning crops into plastics.
What are the characteristics and advantages of polylactic acid?
Completely degradable
Under the action of microorganisms or composting conditions, it can be completely degraded into CO2 and H2O, and the relative biodegradation rate can reach over 90% after 180 days.
Natural antibacterial properties
It has certain inhibition ability to Candida albicans, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Biocompatibility
The raw material lactic acid is an endogenous substance in the human body, and PLA is a human implant material certified by the FDA, which has been widely used in the medical field.
Excellent processability
PLA processing temperature is 170~230 ℃, and various processing methods such as extrusion, stretching, spinning, film blowing, injection molding, blow molding, and blistering can be used for molding.
Non flammability
Non flammable, with an ultimate oxygen index of around 21%, low smoke generation, and no black smoke.
Renewable raw materials
The raw material of PLA comes from biomass carbon sources formed by photosynthesis.
With the gradual enhancement of people’s environmental awareness, biodegradable plastics will replace non environmentally friendly petrochemical raw materials. Faced with the increasing acceptance of biodegradable plastics by society, PLA will achieve penetration in more downstream fields in the future.
Post time: Apr-24-2023